How to Set Up a Successful B2B SEO Strategy
Like most things, SEO is always evolving. As search engine algorithms are updated, requirements and boundaries shift to generate helpful results for internet users. In 2024, B2B SEO strategies rely less on content volume and more on user experience, structured data and unique, expert content. We’re updating this blog to reflect the B2B search marketing strategies that work in 2024.
What is B2B SEO?
Search Engine Optimisation is a digital marketing strategy that aims to increase a website’s organic search engine rankings for target keywords. B2B SEO specifically looks for target keywords for which key decision-makers within businesses are searching.
For example, where a B2C (Business to Customer) business selling coffee would seek to rank for terms like ‘best coffee’, ‘ground coffee’, or ‘organic coffee’, a B2B selling to cafes would target keywords such as ‘wholesale coffee beans’, ‘coffee bean supplier’, and so on.
B2B SEO is one of the most sustainable ways of generating leads for B2B companies. At least 70% of decision-makers start their research and buying process with a general search online. Your target customer is finding their new supplier from search engines.
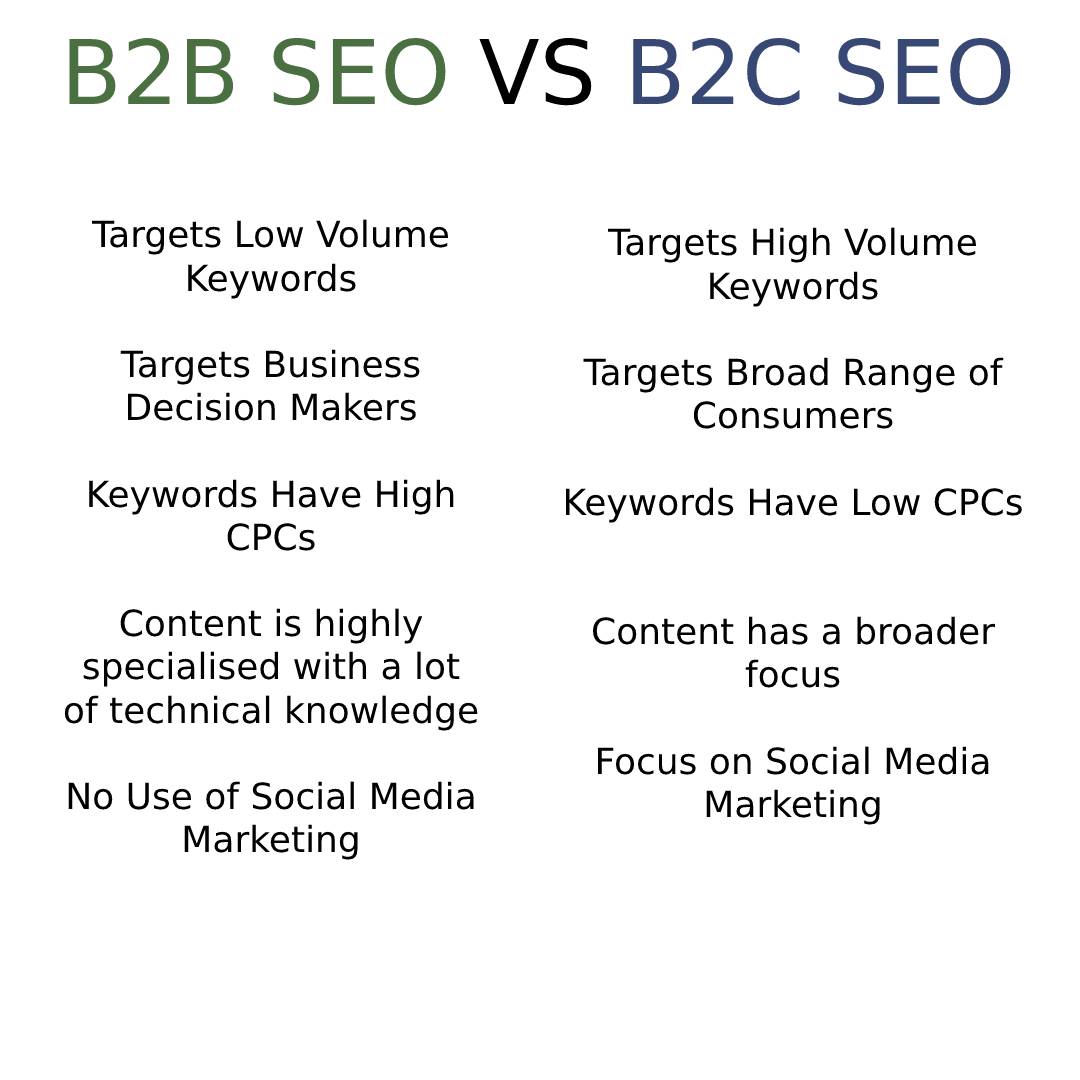
The Difference between B2B & B2C SEO
There is a lot of commonality between B2C & B2B SEO. In both, focus on on-page optimisation, carry out keyword research, build backlinks, improve technical SEO and write SEO-friendly content. Google doesn’t differentiate between B2B and B2C searches, so the ranking factors are the same.
However, B2B has a very different target audience from B2C SEO. A B2B audience is much smaller, has a much higher knowledge of the topic, and have a much narrower demographic.
All this means that the target keywords for B2B SEO have a much lower monthly search volume.
B2B keywords also have high CPC value, because many B2B companies will have more budget to invest in paid search advertising.
-
Understand Your Target Audience
With B2B SEO, figuring out who your target demographics can be a bit more difficult than B2C. It is always easier to plan SEO when you have a good idea of the kind of individual you are targeting. Create a customer persona or profile by answering the following questions about your ideal buyer.
- What industry are they in?
- How big is the business?
- What is their job title?
- How is their job performance measured?
- Who do they report to?
- What level of knowledge will they have on their specific industry?
From this profile, map out some initial ideas for keywords they would search to find your business’s products or services. This can vary a lot from business to business, so it’s difficult to generalise. Keep in mind why this individual needs your businesses to accomplish their goals.
-
Pick the Right Keywords
Build upon your customer profile by going into more depth in your keyword research.
You should aim to meet the following criteria with your target keywords:
- Relevant: The keyword should be relevant to your brand and product/service. Get in the mind frame of a decision maker – what exactly will they be searching to find you?
- Enough Volume: They have enough monthly search volume to make it worth targeting. For B2B, this could be 300, 100 or even 50. Your rates and prices will show how many leads you’ll need to bring value from SEO.
- Reasonable Keyword Difficulty: if the KD is 90, it will take a lot of work to rank for that term. If your budget is low, the KD should be too.
- Manageable Competition: If many companies are bidding for the top paid spaces in search, but you get the top organic spot, you’ve saved money.
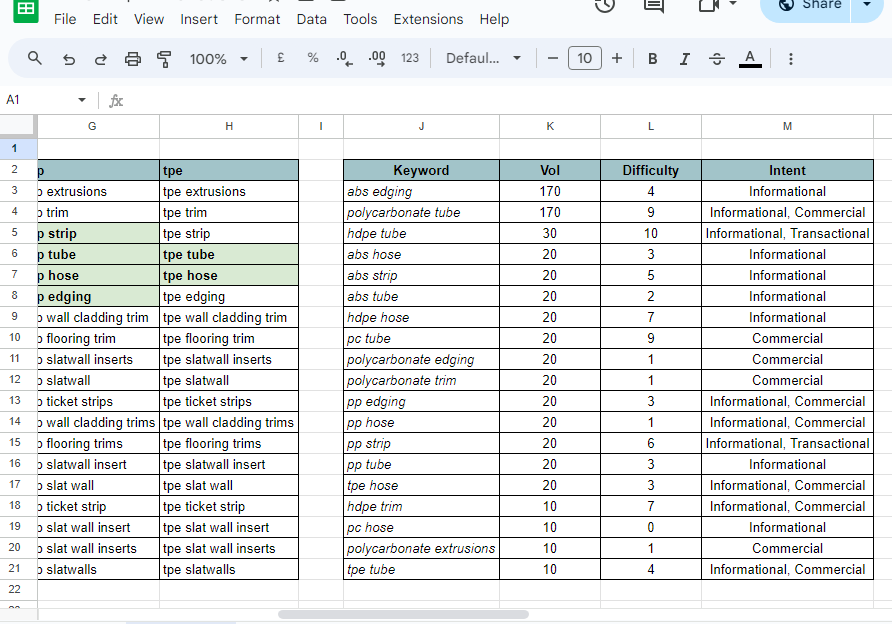
Use these points as a guiding principle, rather than hard and fast rules. Collect keywords in a spreadsheet, together with volume, difficulty, CPC and the URL on your website to which the term relates. This will help you classify and review priorities later on.
Tools for Keyword Research
There are many various tools you can use to research keywords, some of which are right there on the results pages. Tools include:
- Google AutoComplete
- Google’s Related Searches
- Google Keyword Planner
- Google Trends
- SEMRush Keyword Tools (Paid)
- AnswerThePublic
- AlsoAsked (Paid)
- Ahrefs Free Keyword Generator
3. Map Keywords to the Buyer’s Journey
Once you have your list of keywords, you can now map them to the different stages of the buyer’s journey.
This is the marketing funnel that we all know so well, but here’s a quick review of the 4 key stages and how they correspond to SEO.
Each search term has a specific intent behind it, and keywords are organised into Informational, Navigational, Commercial & Transactional search intents. We can pair these loosely with the four funnel stages.
Awareness Stage (Search Intent: Informational)
Awareness is the information-gathering stage, where customers are looking to gain general knowledge about a topic in response to a need within their business. This will most likely apply to your broadest keywords.
Landing pages will typically be Blogs, How to Guides, and FAQs. Successful content will focus on how your product/service fits into their business needs at the broadest level.
Interest Stage (Search Intent: Navigational)
The searcher has carried out initial research and now has an idea in mind as to what product/service they need. Their searches will now be more focused, looking for specific product or service keywords.
Landing pages for this stage will be service pages and product pages. Content will need to include specific product/service keywords with as many variations as possible.
Consideration Stage(Search Intent: Commercial)
The searcher has now found the product and service they want and is carrying out further research if there are any better alternatives. They compare price, service, lead times, reviews etc.
To capture interest at this stage, make sure your website displays unique selling points, including an idea of price, third-party reviews and as much information as possible to ensure that a customer will choose you over a competitor. Comparison posts showing directly the differences between products on the market can be a key type of content to target consumers in the consideration stage.
Conversion Stage (Search Intent: Transactional)
The searcher is aware of your product or service, has considered the options and they are ready to make a purchase.
It’s crucial to make product pages and contact forms easy to find so that users can place an order.
For successful B2B SEO, make sure that you have content and landing pages on your website that target keywords at every stage of the buyer’s journey.
If you find that you are lacking keywords for a certain stage, carry out more keyword research to fill in the gaps.
4. Optimise your Product and Service Pages
Once you have your keywords mapped to important pages, you can begin to optimise them. Your main service and product pages are where compelling copy, effective user experience and technical function come together. Use these pages to showcase your product or service to potential customers, and use the keywords that you have mapped to them.
On-Page Optimisation for B2B
For the majority of on-page optimisation, this will be similar to the steps involved in optimising a B2C website. Follow the below checklist to ensure your pages are optimised fully.
- Optimise Meta Data
- Check Keyword Density
- Optimise H1 & H2 tags
- No broken or redirecting internal links
- Pages should have a crawl depth of no more than 3 pages
- Check pages reach adequate Page Speed Scores
- Include internal linking to relevant pages within the body text
- Fix any technical issues.
- Make sure pages are secure with valid SSL certificates.
- Check canonical tags are present and correct.
- Ensure all pages use SEO-friendly URL structure
- Fix any orphaned pages
- All pages should have relevant structured data
- Images are optimised for SEO
- Make sure all pages are mobile-friendly
The main difference between on-page optimisation for B2C and B2B will be the level of specific information in your content.
B2B search users often have a greater level of experience and knowledge about their search than an average B2C customer. Because of this, you will need to finely tailor your content to your audience by including detail and technical information.
5. Tailor your Content to your Audience
In B2B SEO, search users are likely to be very familiar with your industry, even at the information-gathering stage. They will immediately be able to spot a lack of knowledge on your page.
This is why it’s important to regularly check and add to your content, even if the body and structure are written by an agency. Show your expertise.
Every page should clearly state why you stand out within your industry. Demonstrate why someone should choose to work with your business.
A few ways to do this could be:
- Use social proof such as third-party reviews, industry awards and accreditations to provide assurance and build trust with users.
- Have clear CTAs across your landing pages so users know where to go next.
- Be clear about prices. If you can only show a range or starting price, be as accurate as possible.
- Explain exactly how you can help solve their problems.
As well as improving content across your main website pages, you should be looking to build additional helpful content. SEO is no longer about having hundreds of blog posts in the same format. In 2024, your supporting content should be helpful to users, such as FAQs, user manuals, product comparisons and video content.
Supporting content should also include internal links to your key landing pages.
Don’t Forget the Basics of B2B SEO
Following these steps should put you on the right track towards a winning B2B SEO strategy. However, this isn’t something you do once. After this campaign, you need to build upon its success with backlink building, regular site audits, content plans and monthly performance reviews. Maintaining your gains is a key marketing operation, and requires regular upkeep.